K8s API 核心对象 —— client-go
· ☕ 3 分钟
API 入口
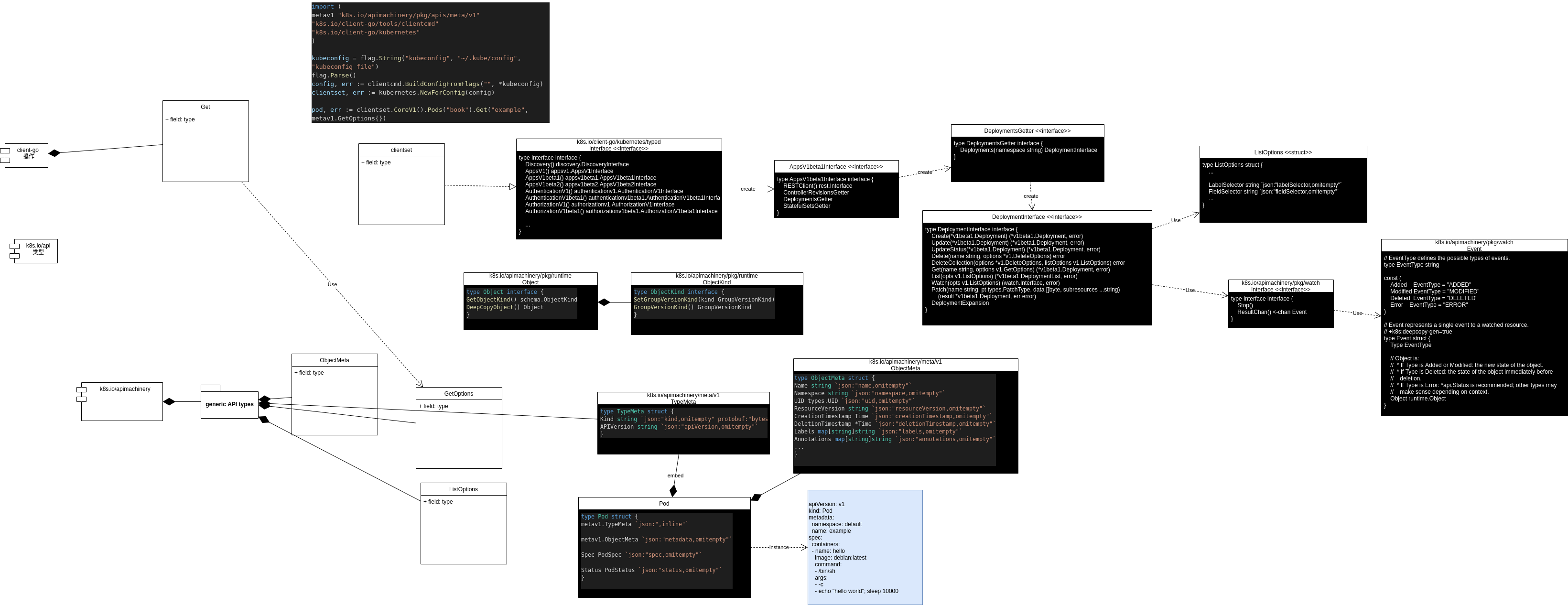
Client Sets
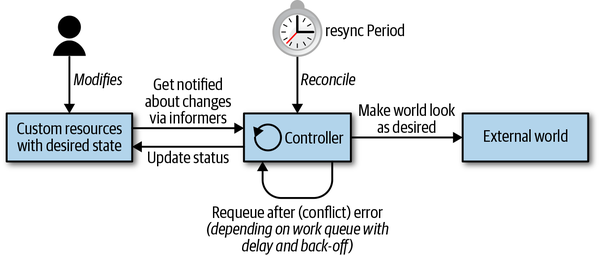
接收变更通知和缓存(Informers and Caching)
Client Sets可以 watch 变更,但一般我们用更高级的 Informers,因为它有缓存、索引等功能。
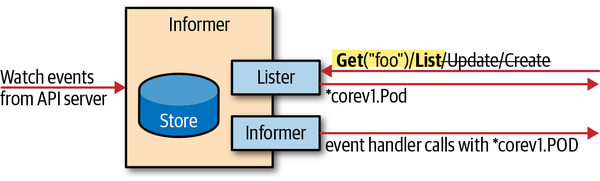
- Lister :被应用调用,返回缓存中的数据列表
- Informer:监听器
Informer 有两个功能

Client Sets
Client Sets可以 watch 变更,但一般我们用更高级的 Informers,因为它有缓存、索引等功能。

Informer 有两个功能
you can also create a chart with dependencies to other charts (a.k.a. umbrella chart) which are completely external using the requirements.yaml file.
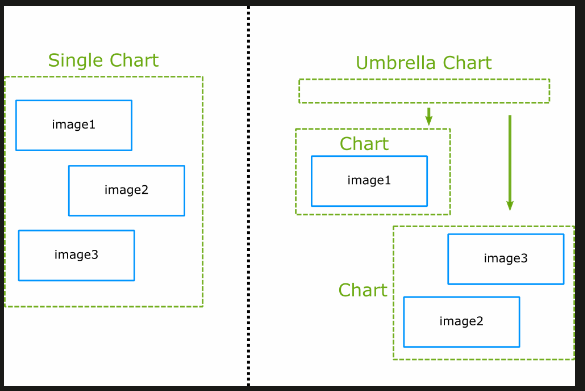
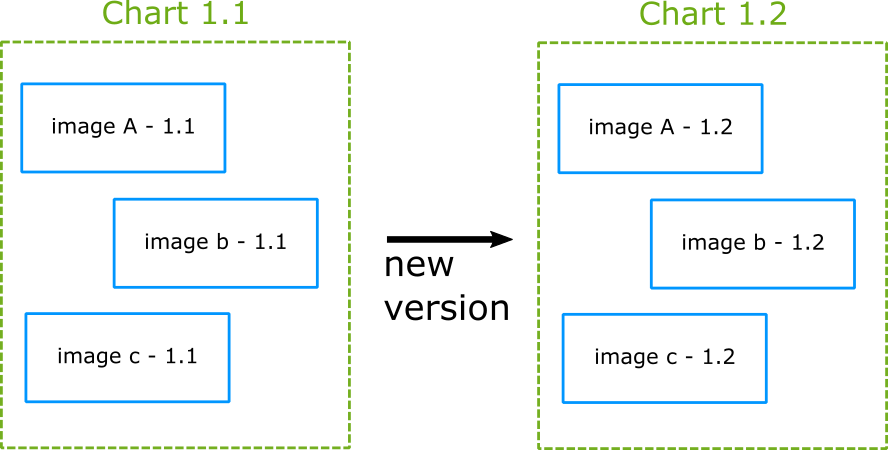
https://codefresh.io/docs/docs/new-helm/helm-best-practices/
最近由于工作需要,重新系统回顾 Kubernetes 的编程。发现《Programming Kubernetes》这书写得比较系统。于是边学,边记录一些重点。
本文状态:草稿
|
|
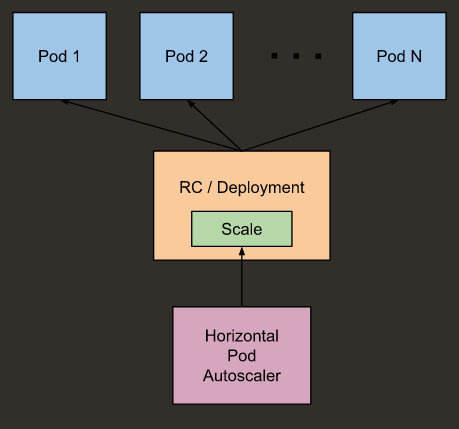
desiredReplicas = ceil[currentReplicas * ( currentMetricValue / desiredMetricValue )]
currentMetricValue 为相关 pod 的 metric 平均数。

共享内存,多进程/线程的运行期设计模式已成主流的今天,你有好奇一下,进程/线程间的怎么同步的吗?大部分人知道,我们用的开发语言,或类库函数库,已经提供了看起来很漂亮的封装。然而在漂亮的面子工程后面,大部分归根到底是要内核 或/和 CPU 硬件去完成这些同步的。而反过来,只要我们理解了内部原理,你就可以快速理解那些漂亮的面子工程,和他们可能的性能问题,进而选择一个适合你的“面子工程”。而这些内部原理,就是同步原语。
VirtualService:
|
|
DestinationRule :
|
|
使用 sourceLabels 规则,可以根据源 pod 的 label 进行路由。这里用了 version 这个 label。即根据pod的应用版本进行路由。
这样的路由规则实际是使用于发起调用方的 sidecar。

程序员有两个世界:
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
|
|
|
|
然后在另外一个终端中
|
|
可以看到在 bpftrace 终端中输出:
From [Understanding The Linux Kernel]
之前我们了解到,Linux 倾向用最多的内存做 Page Cache。这使我们不得不考虑如何在内存不足前回收内存。问题是,回收内存的程序本身也可能有 IO 操作,也可能需要内存。
page cache 中的每个 page 均归属于文件. 这个文件 — 或更精确来说,是文件的 inode 被称为 page 的owner.
Page cahce 的核心数据结构是 addrees_space。一般来说,每个 inode (Kernel 用来存放文件元信息的内存中的数据结构,可以视为一个文件的描述信息)中包含一个 addrees_space 。
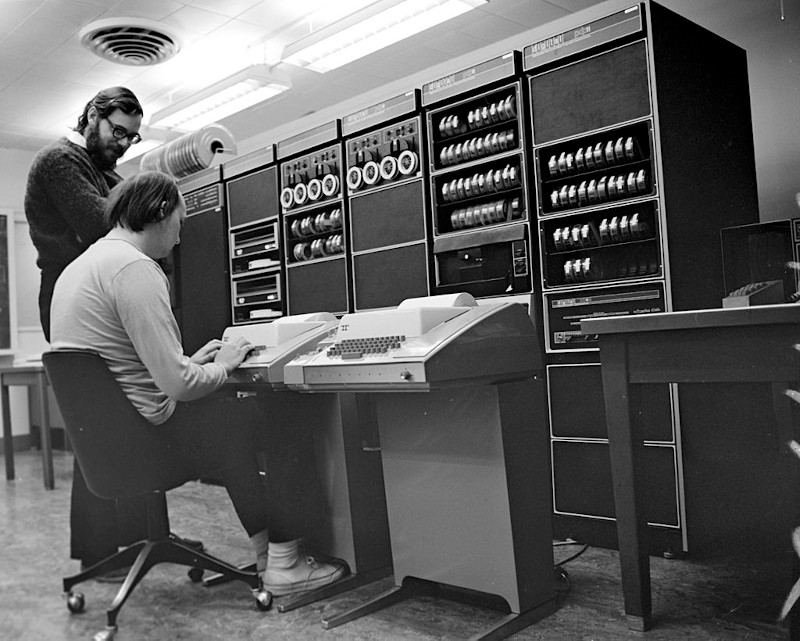

肯尼斯·汤普森(Kenneth Thompson)与丹尼斯·里奇(Dennis Ritchie)一起在AT&T贝尔实验室开发了UNIX。 UNIX操作系统结合了Multics提供的许多分时和文件管理功能,并由此得名。 (Multics是1960年代中期的一个项目,代表了创建多用户,多任务操作系统的第一项努力。)UNIX操作系统迅速赢得了广泛的关注,尤其是在工程师和科学家中。

翻开印象笔记,我回顾了一下最有价值的资料:
Docker/Container 实现原理和架构的入门