寫點東西吧,懒人。
码农幽默英语排行榜 S1E1
· ☕ 3 分钟
缘起
还记得 15 年前,外企还是相当部分程序员的向往。而 2021 了,情况有了相当大的变化。开源界也有相当多的国人开源项目和文档了。所以很多新码农开始提出一个问题:都 2021 了,英文还是码农的基本素养吗?
存储老爷车上云 —— iSCSI简介
· ☕ 5 分钟
Benchmark Tools
· ☕ 1 分钟
CPU Benchmark
The SysBench system benchmark suite has a simple CPU benchmark tool that calculates prime numbers. For example:
# sysbench --num-threads=8 --test=cpu --cpu-max-prime=100000 run
sysbench 0.4.12: multi-threaded system evaluation benchmark
Running the test with following options:
Number of threads: 8
Doing CPU performance benchmark
Threads started!
Done.
Maximum prime number checked in CPU test: 100000
Test execution summary:
total time: 30.4125s
total number of events: 10000
total time taken by event execution: 243.2310
per-request statistics:
min: 24.31ms
avg: 24.32ms
max: 32.44ms
approx. 95 percentile: 24.32ms
Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 1250.0000/1.22
execution time (avg/stddev): 30.4039/0.01
This executed eight threads, with a maximum prime number of 100,000. The runtime was 30.4 s, which can be used for comparison with the results from other systems or configurations (assuming many things, such as that identical compiler options were used to build the software; see Chapter 12, Benchmarking).
tty
· ☕ 3 分钟
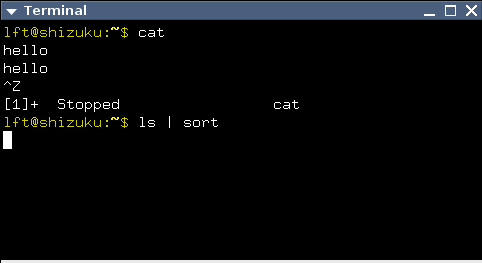
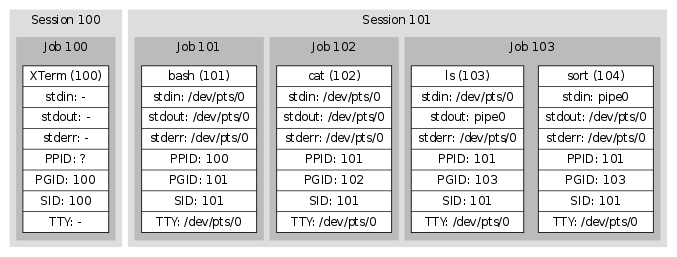
Jobs
-
SIGHUP- 默认动作:Terminate
- 可能动作:Terminate, Ignore, Function call
当检测到 hangup 时,UART 驱动会向整个 session 发送 SIGHUP 信号。 正常情况下,这会 kill 掉所有进程。某些程序,例如
nohup(1)和screen(1),会从他们的 session(和 TTY)中 detach 出来, 因此这些程序的子进程无法关注到 hangup 事件。
Java 内置 Class Loader
· ☕ 3 分钟
内置 Classloader
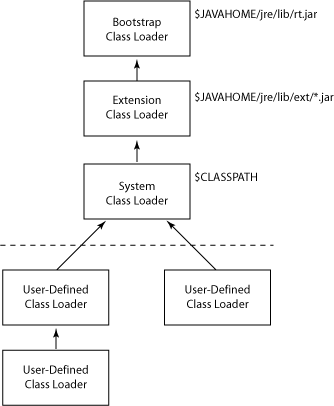
Class loaders load classes and resources present on their respective classpath:
- System or application class loaders load classes from the application classpath
- Extension class loaders search on the Extension classpath (JRE/lib/ext)
- Bootstrap class loader looks on the Bootstrap classpath (JRE/lib/rt.jar)
We can customize the default class loading behavior as well. We can explicitly specify the class loader while loading a class dynamically.
However, we should note that if we load the same class from different types of class loaders, these will be seen as different resources by the JVM.
Opentelemetry Java Agent 浅度解构
· ☕ 2 分钟
Conf
Creating spans around methods with otel.instrumentation.methods.include
Format is "java -Dotel.instrumentation.methods.include=my.package.MyClass1[method1,method2];my.package.MyClass2[method3]"
Classloader
[arthas@16908]$ classloader -t
+-BootstrapClassLoader
+-io.opentelemetry.javaagent.bootstrap.AgentClassLoader@379619aa
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@41fa769c
+-com.taobao.arthas.agent.ArthasClassloader@3697b340
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@71b2d611
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@69cd1085
| +-WebAppClassLoader=266661735@fe4ef67
| | +-com.mycom.sig.foundation.servicediscovery.ExtendedClassLoader@573f7aae
| +-WebAppClassLoader=Server Initiated@1ccb04b3
| | +-com.mycom.sig.foundation.servicediscovery.ExtendedClassLoader@4b3b9a06
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@73cb9ccb
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@7c380e94
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@69ec5d1f
| +-WebAppClassLoader=OAuth Server@10d98940
| | +-com.mycom.ece.common.svcfinder.ExtendedClassLoader@3528968e
| | +-com.mycom.sig.foundation.servicediscovery.ExtendedClassLoader@2919aff3
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@1b0e6bac
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@2f12d8d1
| | +-jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader@73123f21
| +-WebAppClassLoader=1133988396@43974a2c
| +-com.mycom.sig.foundation.servicediscovery.ExtendedClassLoader@39d87c5f
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@1b4c457c
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@3a477cf5
Affect(row-cnt:24) cost in 31 ms.
[arthas@16908]$ classloader
name numberOfInstances loadedCountTotal
org.eclipse.jetty.webapp.WebAppClassLoader 4 24687
BootstrapClassLoader 1 4341
io.opentelemetry.javaagent.bootstrap.AgentClassLoader 1 3502
com.taobao.arthas.agent.ArthasClassloader 1 1430
java.net.URLClassLoader 4 1252
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader 1 570
sun.reflect.DelegatingClassLoader 378 378
sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader 1 56
jnr.ffi.provider.jffi.AsmClassLoader 6 8
com.mycom.sig.foundation.servicediscovery.ExtendedClassLoader 4 6
com.mycom.ece.common.svcfinder.ExtendedClassLoader 1 1
|
|
[arthas@16908]$ sc io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodInstrumentationModule
io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodInstrumentationModule
Affect(row-cnt:1) cost in 54 ms.
[arthas@16908]$ sc -d io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodInstrumentationModule
class-info io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodInstrumentationModule
code-source /
name io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodInstrumentationModule
isInterface false
isAnnotation false
isEnum false
isAnonymousClass false
isArray false
isLocalClass false
isMemberClass false
isPrimitive false
isSynthetic false
simple-name MethodInstrumentationModule
modifier public
annotation
interfaces
super-class +-io.opentelemetry.javaagent.tooling.InstrumentationModule
+-java.lang.Object
class-loader +-io.opentelemetry.javaagent.bootstrap.AgentClassLoader@379619aa
classLoaderHash 379619aa
[arthas@16908]$ sc -d io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodTracer
class-info io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodTracer
code-source
name io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodTracer
isInterface false
isAnnotation false
isEnum false
isAnonymousClass false
isArray false
isLocalClass false
isMemberClass false
isPrimitive false
isSynthetic false
simple-name MethodTracer
modifier public
annotation
interfaces
super-class +-io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.tracer.BaseTracer
+-java.lang.Object
class-loader +-WebAppClassLoader=Server Initiated@1ccb04b3
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@69cd1085
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@41fa769c
classLoaderHash 1ccb04b3
class-info io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodTracer
code-source
name io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.methods.MethodTracer
isInterface false
isAnnotation false
isEnum false
isAnonymousClass false
isArray false
isLocalClass false
isMemberClass false
isPrimitive false
isSynthetic false
simple-name MethodTracer
modifier public
annotation
interfaces
super-class +-io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.tracer.BaseTracer
+-java.lang.Object
class-loader +-WebAppClassLoader=OAuth Server@10d98940
+-java.net.URLClassLoader@69cd1085
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@41fa769c
classLoaderHash 10d98940
shaded
io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.config.Config
->
sc -d io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.config.Config
[arthas@16908]$ sc -d io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.config.Config
class-info io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.config.Config
code-source
name io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation.api.config.Config
isInterface false
isAnnotation false
isEnum false
isAnonymousClass false
isArray false
isLocalClass false
isMemberClass false
isPrimitive false
isSynthetic false
simple-name Config
modifier abstract,public
annotation
interfaces
super-class +-java.lang.Object
class-loader
classLoaderHash null
K8s Custom Resources(CR)
· ☕ 2 分钟
Custom Resource 的入口
请求是这样分发到 api 扩展点的:
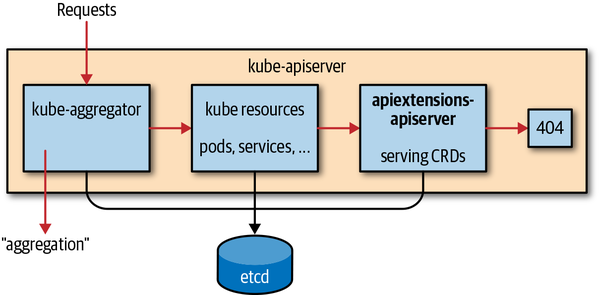
例如我们有 (Custom Resource)CR
|
|
相应的 CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) 会是这样:
K8s API 核心对象 —— client-go
· ☕ 3 分钟
API 入口
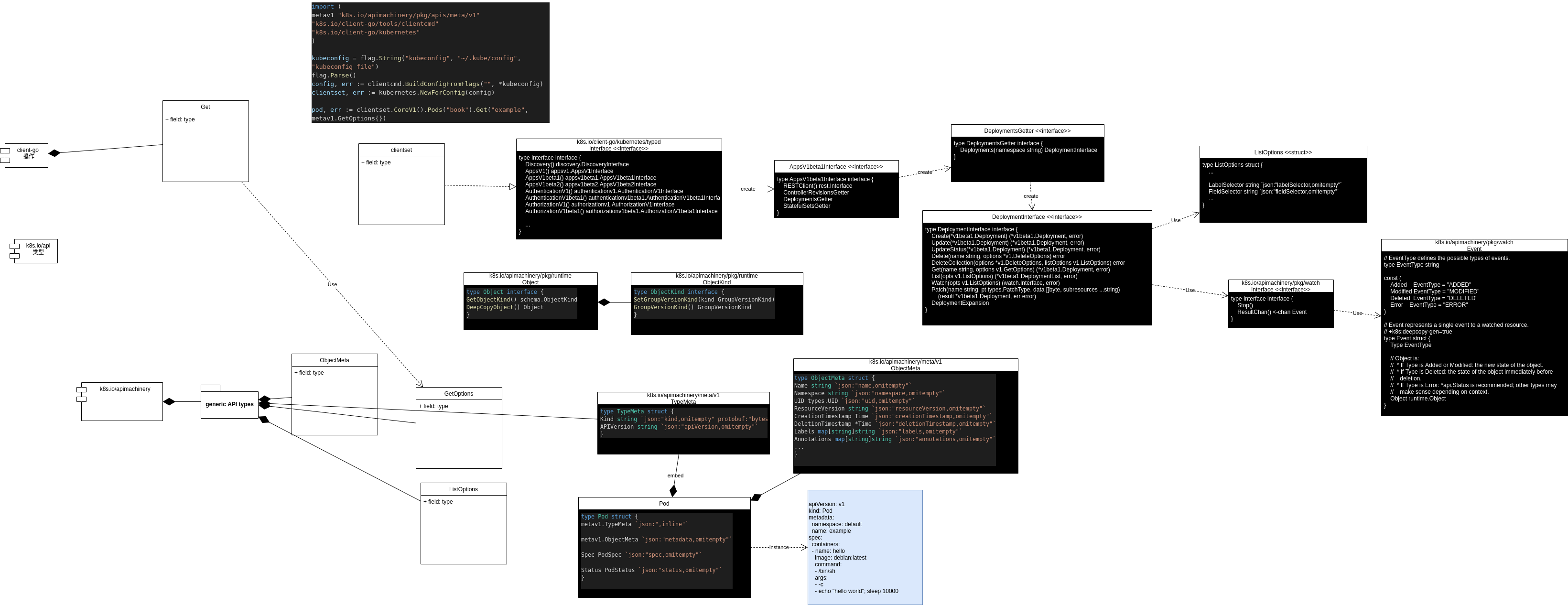
Client Sets
接收变更通知和缓存(Informers and Caching)
Client Sets可以 watch 变更,但一般我们用更高级的 Informers,因为它有缓存、索引等功能。
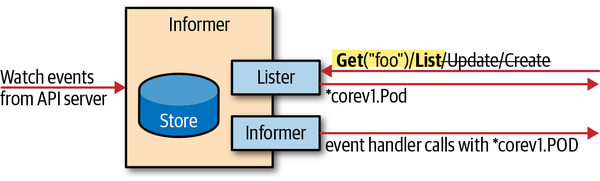
- Lister :被应用调用,返回缓存中的数据列表
- Informer:监听器
Informer 有两个功能
Helm base
· ☕ 1 分钟
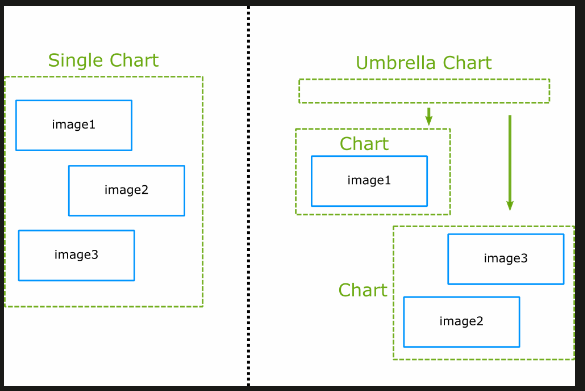
Concept
umbrella chart
you can also create a chart with dependencies to other charts (a.k.a. umbrella chart) which are completely external using the requirements.yaml file.
versioning
Simple 1-1 versioning
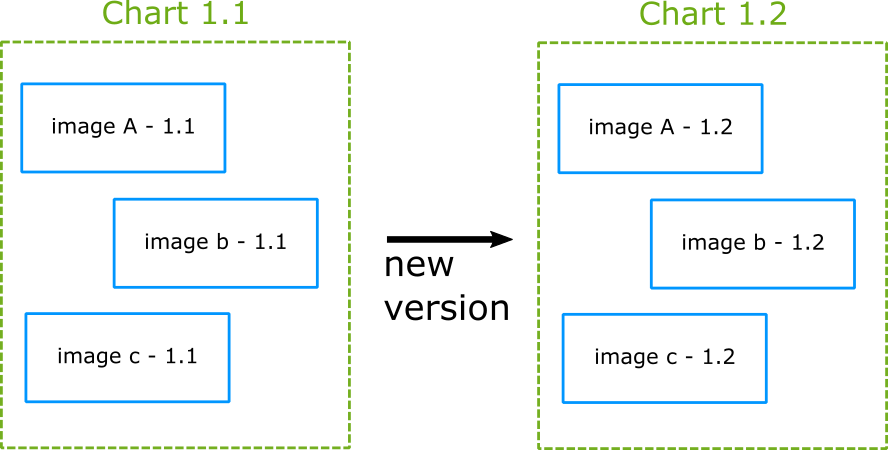
Chart versus application versioning
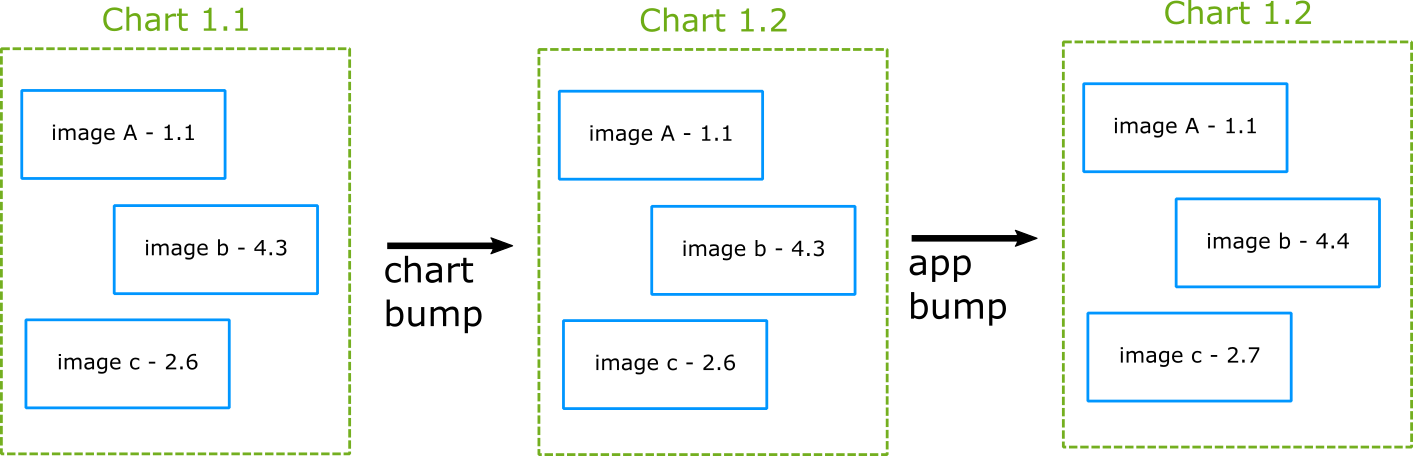
参考
https://codefresh.io/docs/docs/new-helm/helm-best-practices/
Kubernetes extends concept
· ☕ 3 分钟
前言
最近由于工作需要,重新系统回顾 Kubernetes 的编程。发现《Programming Kubernetes》这书写得比较系统。于是边学,边记录一些重点。
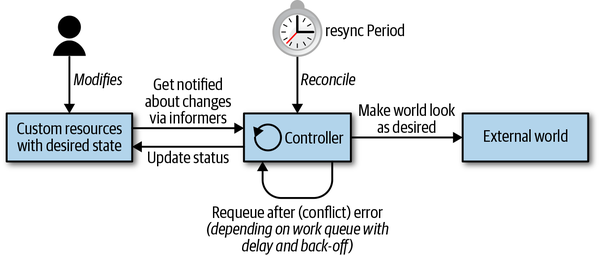
Controller
Controller Loop
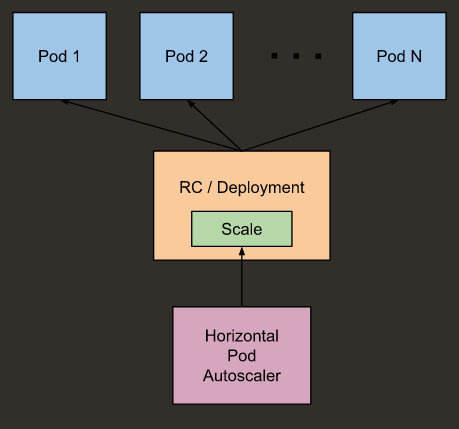
Kubernetes 自动扩缩容
· ☕ 1 分钟
本文状态:草稿
配置例子
|
|
算法
desiredReplicas = ceil[currentReplicas * ( currentMetricValue / desiredMetricValue )]
currentMetricValue 为相关 pod 的 metric 平均数。